全面认识 Nginx

全面认识 Nginx
鱼六秒Nginx 特点
- 高并发、高性能
- 模块化架构使得它的扩展性非常好
- 异步非阻塞的事件驱动模型这点和 Node.js 相似
- 相对于其它服务器来说它可以连续几个月甚至更长而不需要重启服务器使得它具有高可靠性
- 热部署、平滑升级
- 完全开源,生态繁荣
Nginx 作用
Nginx 的最重要的几个使用场景:
- 静态资源服务,通过本地文件系统提供服务
- 反向代理服务,延伸出包括缓存、负载均衡等
- API 服务, OpenResty
对于前端来说Node.js并不陌生,Nginx和Node.js的很多理念类似,HTTP服务器、事件驱动、异步非阻塞等,且Nginx的大部分功能使用Node.js也可以实现,但Nginx和Node.js并不冲突,都有自己擅长的领域。Nginx擅长于底层服务器端资源的处理(静态资源处理转发、反向代理,负载均衡等),Node.js更擅长上层具体业务逻辑的处理,两者可以完美组合
用一张图表示:
Nginx 常用命令
systemctl 系统命令:
1 | # 开机配置 |
Nginx 应用程序命令:
1 | nginx -s reload # 向主进程发送信号,重新加载配置文件,热重启 |
Nginx 核心配置
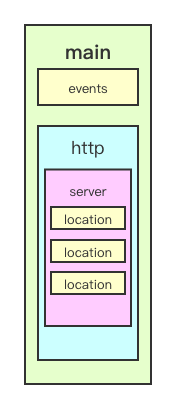
配置文件结构
Nginx 的典型配置示例:
1 | # main段配置信息 |
全局配置,对全局生效
- events 配置影响 Nginx 服务器与用户的网络连接
- http 配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置
- server 配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个 http 块中可以有多个 server 块
- location 用于配置匹配的 uri
- upstream 配置后端服务器具体地址,负载均衡配置不可或缺的部分
用一张图清晰的展示它的层级结构:
配置文件 main 段核心参数
user
指定运行 Nginx 的 woker 子进程的属主和属组,其中组可以不指定。
1 | user USERNAME [GROUP] |
pid
指定运行 Nginx master 主进程的 pid 文件存放路径。
1 | pid /opt/nginx/logs/nginx.pid # master主进程的的pid存放在nginx.pid的文件 |
worker_rlimit_nofile_number
指定 worker 子进程可以打开的最大文件句柄数。
1 | worker_rlimit_nofile 20480; # 可以理解成每个worker子进程的最大连接数量。 |
worker_rlimit_core
指定 worker 子进程异常终止后的 core 文件,用于记录分析问题。
1 | worker_rlimit_core 50M; # 存放大小限制 |
worker_processes_number
指定 Nginx 启动的 worker 子进程数量。
1 | worker_processes 4; # 指定具体子进程数量 |
worker_cpu_affinity
将每个 worker 子进程与我们的 cpu 物理核心绑定。
1 | worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000; # 4个物理核心,4个worker子进程 |
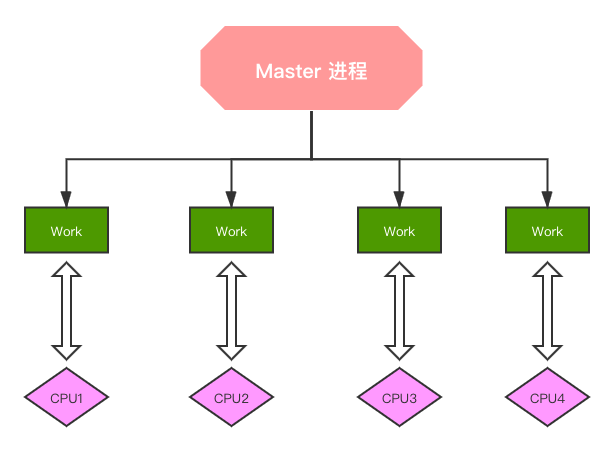
将每个 worker 子进程与特定 CPU 物理核心绑定,优势在于,避免同一个 worker 子进程在不同的 CPU 核心上切换,缓存失效,降低性能。但其并不能真正的避免进程切换。worker_priority
指定 worker 子进程的 nice 值,以调整运行 Nginx 的优先级,通常设定为负值,以优先调用 Nginx 。
1 | worker_priority -10; # 120-10=110,110就是最终的优先级 |
Linux 默认进程的优先级值是120,值越小越优先;nice 定范围为 -20 到 +19 。
应用的默认优先级值是120加上 nice 值等于它最终的值,这个值越小,优先级越高。
worker_shutdown_timeout
指定 worker 子进程优雅退出时的超时时间。
1 | worker_shutdown_timeout 5s; |
timer_resolutionworker 子进程内部使用的计时器精度,调整时间间隔越大,系统调用越少,有利于性能提升;反之,系统调用越多,性能下降。
1 | timer_resolution 100ms; |
在 Linux 系统中,用户需要获取计时器时需要向操作系统内核发送请求,有请求就必然会有开销,因此这个间隔越大开销就越小。daemon
指定 Nginx 的运行方式,前台还是后台,前台用于调试,后台用于生产。
1 | daemon off; # 默认是on,后台运行模式 |
配置文件 events 段核心参数
useNginx 使用何种事件驱动模型。
1 | use method; # 不推荐配置它,让nginx自己选择 |
worker_connectionsworker 子进程能够处理的最大并发连接数。
1 | worker_connections 1024 # 每个子进程的最大连接数为1024 |
accept_mutex
是否打开负载均衡互斥锁。
1 | accept_mutex on # 默认是off关闭的,这里推荐打开 |
server_name 指令
指定虚拟主机域名。
1 | server_name name1 name2 name3 |
域名匹配的四种写法:
- 精确匹配:server_name www.nginx.com ;
- 左侧通配:server_name *.nginx.com ;
- 右侧统配:server_name www.nginx.* ;
- 正则匹配:server_name ~^www.nginx.*$ ;
匹配优先级:精确匹配>左侧通配符匹配>右侧通配符匹配>正则表达式匹配server_name配置实例:
配置本地
DNS解析vim /etc/hosts1
2
3
4
5
6
7# 添加如下内容,其中 121.42.11.34 是阿里云服务器IP地址
121.42.11.34 www.nginx-test.com
121.42.11.34 mail.nginx-test.com
121.42.11.34 www.nginx-test.org
121.42.11.34 doc.nginx-test.com
121.42.11.34 www.nginx-test.cn
121.42.11.34 fe.nginx-test.club这里使用的是虚拟域名进行测试,因此需要配置本地 DNS 解析,如果使用阿里云上购买的域名,则需要在阿里云上设置好域名解析
配置阿里云
Nginx,vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41# 这里只列举了http端中的sever端配置
# 左匹配
server {
listen 80;
server_name *.nginx-test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/left-match/;
location / {
index index.html;
}
}
# 正则匹配
server {
listen 80;
server_name ~^.*\.nginx-test\..*$;
root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/reg-match/;
location / {
index index.html;
}
}
# 右匹配
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.nginx-test.*;
root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/right-match/;
location / {
index index.html;
}
}
# 完全匹配
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.nginx-test.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html/nginx-test/all-match/;
location / {
index index.html;
}
}访问分析
- 当访问
www.nginx-test.com时,都可以被匹配上,因此选择优先级最高的“完全匹配” - 当访问
mail.nginx-test.com时,会进行“左匹配” - 当访问
www.nginx-test.org时,会进行“右匹配” - 当访问
doc.nginx-test.com时,会进行“左匹配” - 当访问
www.nginx-test.cn时,会进行“右匹配” - 当访问
fe.nginx-test.club时,会进行“正则匹配”root
指定静态资源目录位置,它可以写在http、server、location等配置中。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8root path
例如:
location /image {
root /opt/nginx/static;
}
当用户访问 www.test.com/image/1.png 时,实际在服务器找的路径是 /opt/nginx/static/image/1.pngroot会将定义路径与URI叠加,alias则只取定义路径。
alias
它也是指定静态资源目录位置,它只能写在 location 中。
1 | location /image { |
使用 alias 末尾一定要添加 / ,并且它只能位于 location 中。
location
配置路径。
1 | location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { |
匹配规则:
- = 精确匹配;
- ~ 正则匹配,区分大小写
- ~* 正则匹配,不区分大小写
- ^~ 匹配到即停止搜索;
匹配优先级:= > ^~ > ~ > ~* > 不带任何字符。
实例:
1 | server { |
location 中的反斜线
1 | location /test { |
- 不带
/当访问www.nginx-test.com/test时,Nginx先找是否有test目录,如果有则找test目录下的index.html;如果没有test目录,nginx则会找是否有test文件。 - 带
/当访问www.nginx-test.com/test时,Nginx先找是否有test目录,如果有则找test目录下的index.html,如果没有它也不会去找是否存在test文件。return
停止处理请求,直接返回响应码或重定向到其他URL;执行return指令后,location中后续指令将不会被执行。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20return code [text];
return code URL;
return URL;
例如:
location / {
return 404; # 直接返回状态码
}
location / {
return 404 "pages not found"; # 返回状态码 + 一段文本
}
location / {
return 302 /bbs ; # 返回状态码 + 重定向地址
}
location / {
return https://www.baidu.com ; # 返回重定向地址
}rewrite
根据指定正则表达式匹配规则,重写URL。1
2
3
4
5语法:rewrite 正则表达式 要替换的内容 [flag];
上下文:server、location、if
示例:rewirte /images/(.*\.jpg)$ /pic/$1; # $1是前面括号(.*\.jpg)的反向引用 flag可选值的含义:last重写后的URL发起新请求,再次进入server段,重试location的中的匹配;break直接使用重写后的URL,不再匹配其它location中语句;redirect返回302临时重定向;permanent返回301永久重定向按照这个配置我们来分析:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20server{
listen 80;
server_name fe.lion.club; # 要在本地hosts文件进行配置
root html;
location /search {
rewrite ^/(.*) https://www.baidu.com redirect;
}
location /images {
rewrite /images/(.*) /pics/$1;
}
location /pics {
rewrite /pics/(.*) /photos/$1;
}
location /photos {
}
}- 当访问
fe.lion.club/search时,会自动帮我们重定向到https://www.baidu.com。 - 当访问
fe.lion.club/images/1.jpg时,第一步重写URL为fe.lion.club/pics/1.jpg,找到pics的location,继续重写URL为fe.lion.club/photos/1.jpg,找到/photos的location后,去html/photos目录下寻找1.jpg静态资源
if 指令
1 | 语法:if (condition) {...} |
condition 判断条件:
$variable仅为变量时,值为空或以0开头字符串都会被当做false处理=或!=相等或不等~正则匹配! ~非正则匹配~*正则匹配,不区分大小写-f或! -f检测文件存在或不存在-d或! -d检测目录存在或不存在-e或! -e检测文件、目录、符号链接等存在或不存在-x或! -x检测文件可以执行或不可执行
实例:当访问1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
root html;
location / {
if ( $uri = "/images/" ){
rewrite (.*) /pics/ break;
}
}
}localhost:8080/images/时,会进入if判断里面执行rewrite命令。autoindex
用户请求以/结尾时,列出目录结构,可以用于快速搭建静态资源下载网站。autoindex.conf配置信息:当访问1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13server {
listen 80;
server_name fe.lion-test.club;
location /download/ {
root /opt/source;
autoindex on; # 打开 autoindex,,可选参数有 on | off
autoindex_exact_size on; # 修改为off,以KB、MB、GB显示文件大小,默认为on,以bytes显示出⽂件的确切⼤⼩
autoindex_format html; # 以html的方式进行格式化,可选参数有 html | json | xml
autoindex_localtime off; # 显示的⽂件时间为⽂件的服务器时间。默认为off,显示的⽂件时间为GMT时间
}
}fe.lion.com/download/时,会把服务器/opt/source/download/路径下的文件展示出来,如下图所示:
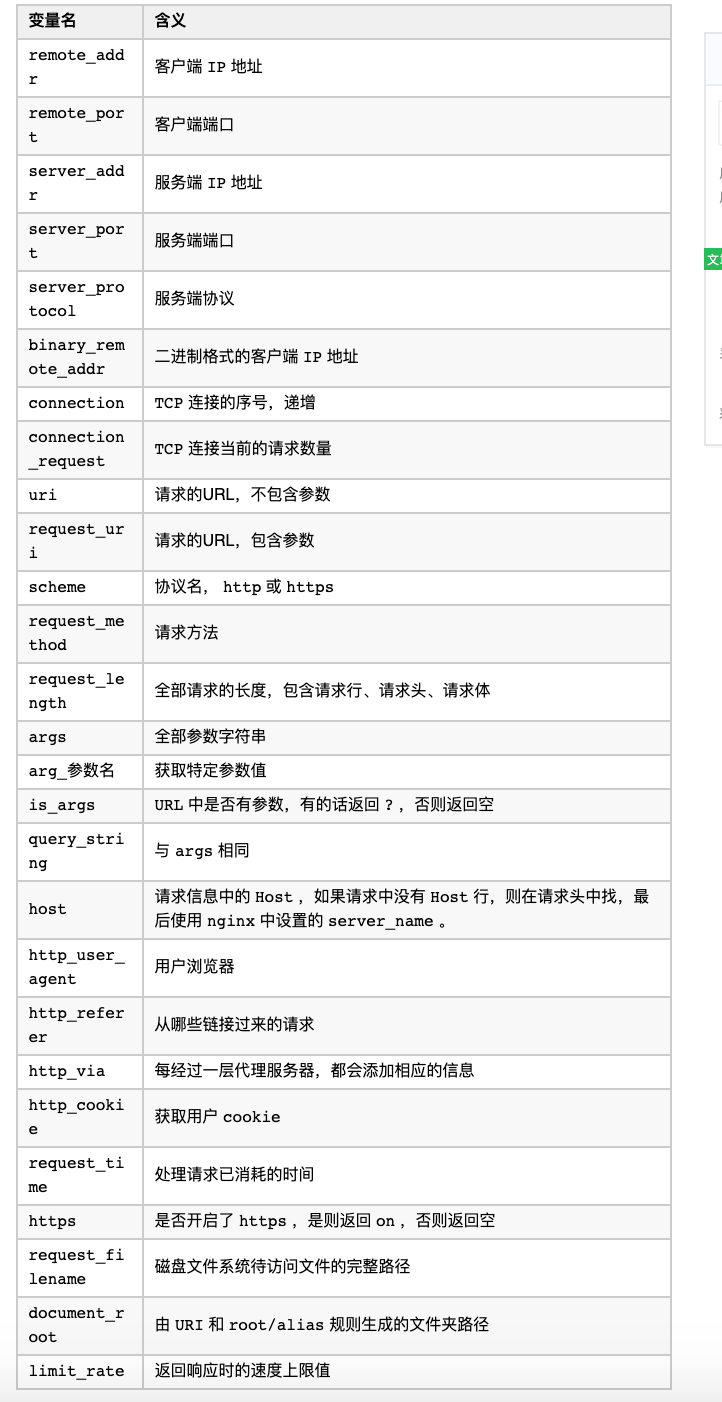
变量
Nginx 提供给使用者的变量非常多,但是终究是一个完整的请求过程所产生数据, Nginx 将这些数据以变量的形式提供给使用者。
下面列举些项目中常用的变量:
实例演示 var.conf :
1 | server{ |
当我们访问 http://var.lion-test.club:8081/test?pid=121414&cid=sadasd 时,由于 Nginx 中写了 return 方法,因此 chrome 浏览器会默认为我们下载一个文件,下面展示的就是下载的文件内容:
1 | remote_addr: 27.16.220.84 |
Nginx 的配置还有非常多,以上只是罗列了一些常用的配置,在实际项目中还是要学会查阅文档。