python-ctype库

python-ctype库
鱼六秒ctypes是一个超级强大的Python库
ctypes 是 Python 的外部函数库。它提供了与 C 兼容的数据类型,并允许调用 DLL 或共享库中的函数。可使用该模块以纯 Python 形式对这些库进行封装。
最近要使用python调用C++编译生成的DLL动态链接库,因此学习了一下ctypes库的基本使用
一、重点讲解 调用方式 和 导出
在Windows上动态库是dll文件,在linux上动态库是so文件。下面以windows上的操作为例
C++ 的函数现有两种调用约定:__cdecl 和 __stdcall
ctypes.CDLL() 和 ctypes.WinDLL() 加载DLL方式
其对应的python ctypes有两种加载方法,如下
| c++ 函数调用方式 | python ctypes加载方式 | |
|---|---|---|
| __cdecl | ctypes.CDLL(dll名字) | dll = CDLL(r’MFCLibrary1.dll’) |
| __stdcall | ctypes.WinDLL(dll名字) | dll = WinDLL(r’MFCLibrary1.dll’) |
c++ 函数的调用声明方式
前两种为 __cdecl, 最后一种为 __stdcall
1 | extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) int test2(std::string test_string); //c++默认 __cdecl py:ctypes.CDLL |
| 标志 | 作用 | |
|---|---|---|
| extern “C” | 是为了不改名,函数仅加 _ 下划线 | 必须使用,否则编译器会把函数改名. |
| __declspec(dllexport) | 是为了导出函数,可以被外部找到 | 否则 dll 外部无法找到 |
| __cdecl | vs 默认的调用约定 | 上述 test2 函数没有该标志,其实默认就如此,用cytpes.CDll加载 |
| __stdcall | stdcall调用约定 | 需要使用 ctype.WinDll 加载dll 才可以 |
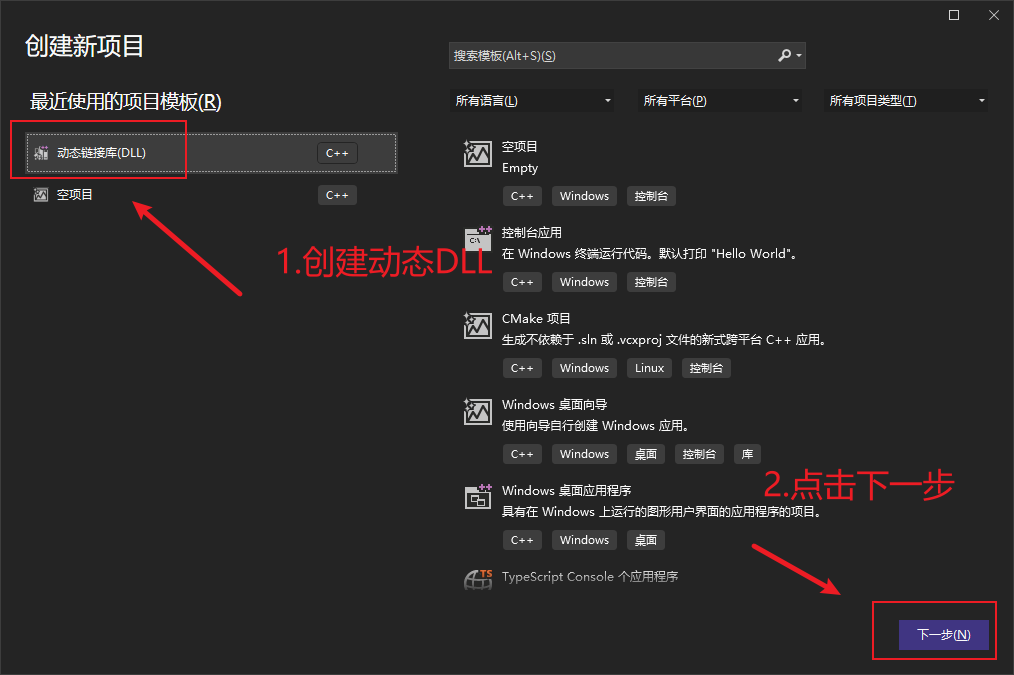
二、Python 调用 C/C++
用visual stdio创建动态链接库
- 新建动态链接库项目
- 新建
main.cpp文件
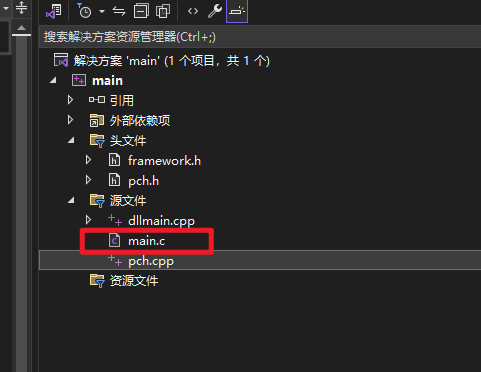
main.cpp中添加include “pch.h”另外函数的前面都加上_declspec(dllexport)前缀。Ctrl+b后就可以生成dll文件dll文件所在路径:E:\main\x64\Debug\main.dll
main.c
1 |
|
python中调用方法如下。首先加载dll文件。然后调用其中的方法
1 | from ctypes import * |
函数参数的 ctypes数据类型
ctypes定义了一些和C兼容的基本数据类型:
| ctypes 类型 | C 类型 | Python 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| c_bool | _Bool | bool (1) |
c_char |
char | 单字符字节串对象1-character string |
c_wchar |
wchar_t | 单字符字符串1-character string |
c_byte |
char | int |
c_ubyte |
unsigned char | int |
c_short |
short | int |
c_ushort |
unsigned short | int |
c_int |
int | int |
c_uint |
unsigned int | int |
c_long |
long | int |
c_ulong |
unsigned long | int |
c_longlong |
__int64 or long long | int |
c_ulonglong |
unsigned __int64 or unsigned long long | int |
c_size_t |
size_t | int |
c_ssize_t |
ssize_t or Py_ssize_t | int |
c_float |
float | float |
c_double |
double | float |
c_longdouble |
long double | float |
c_char_p |
char* (NUL terminated) | 字节串对象或 None |
c_wchar_p |
wchar_t* (NUL terminated) | 字符串或 None |
c_void_p |
void* | int 或 None |
根据c语言中的函数,参数传递,参数返回等特性,总结了7大使用场景
场景一:c函数无输入参数,返回一个整数
c代码如下
1 |
|
Python中的调用restype指定了函数的返回类型,是int类型。然后直接调用函数,获取返回值
1 | from ctypes import * |
场景二:c函数无输入参数,返回一个整数类型的指针
c代码如下
1 |
|
Python代码 restype指定为POINTER(c_int),获取到返回值
1 | from ctypes import * |
场景三:c函数无输入参数,返回一个指向整数类型的指针的指针
1 | DLLEXPORT int ** test_int_p() |
Python代码 restype指定为POINTER(POINTER(c_int)),获取到返回值
1 | from ctypes import * |
场景四:c函数 两个int类型的参数,返回一个整数
1 | DLLEXPORT int test_para(int a, int b) |
因为函数有两个输入参数,因此argtypes就是传入函数的输入参数类型
1 | from ctypes import * |
场景五: c函数接受2个int类型的指针,一个char类型的指针
c代码如下
1 | DLLEXPORT int test_para_p(int* a, int* b, const char* str) |
参数默认情况下是按值传递的,而不是按引用传递。
但是在你的 C 函数中,你希望传递指向整数的指针作为参数,因此需要通过引用传递这些指针。
因此 使用 byref 函数,它将创建指向参数的指针,并将其传递给函数,
使用 byref 的目的是确保在调用 C 函数时传递指向整数的指针,从而允许 C 函数修改这些整数的值
python代码如下
argtypes和restype的使用方式没有变化python中将整数转换成指针的方式是通过ctypes.byref(arg1)的方式
1 | from ctypes import * |
场景六:c函数接收一个结构体指针,并返回这个结构体指针
c代码如下
1 | // 定义了一个名为 MyStruct 的结构体 |
Python代码
1 | from ctypes import * |
场景七:c函数接收一个结构体指针,这个结构体中有一个字符串数组
c代码如下
1 | struct MyStruct1 |
python代码如下
1 | from ctypes import * |
场景八:c函数接收一个结构体指针,该结构体是一个链表。
c代码如下:
1 | struct Yu { |
python代码如下:
1 | from ctypes import * |